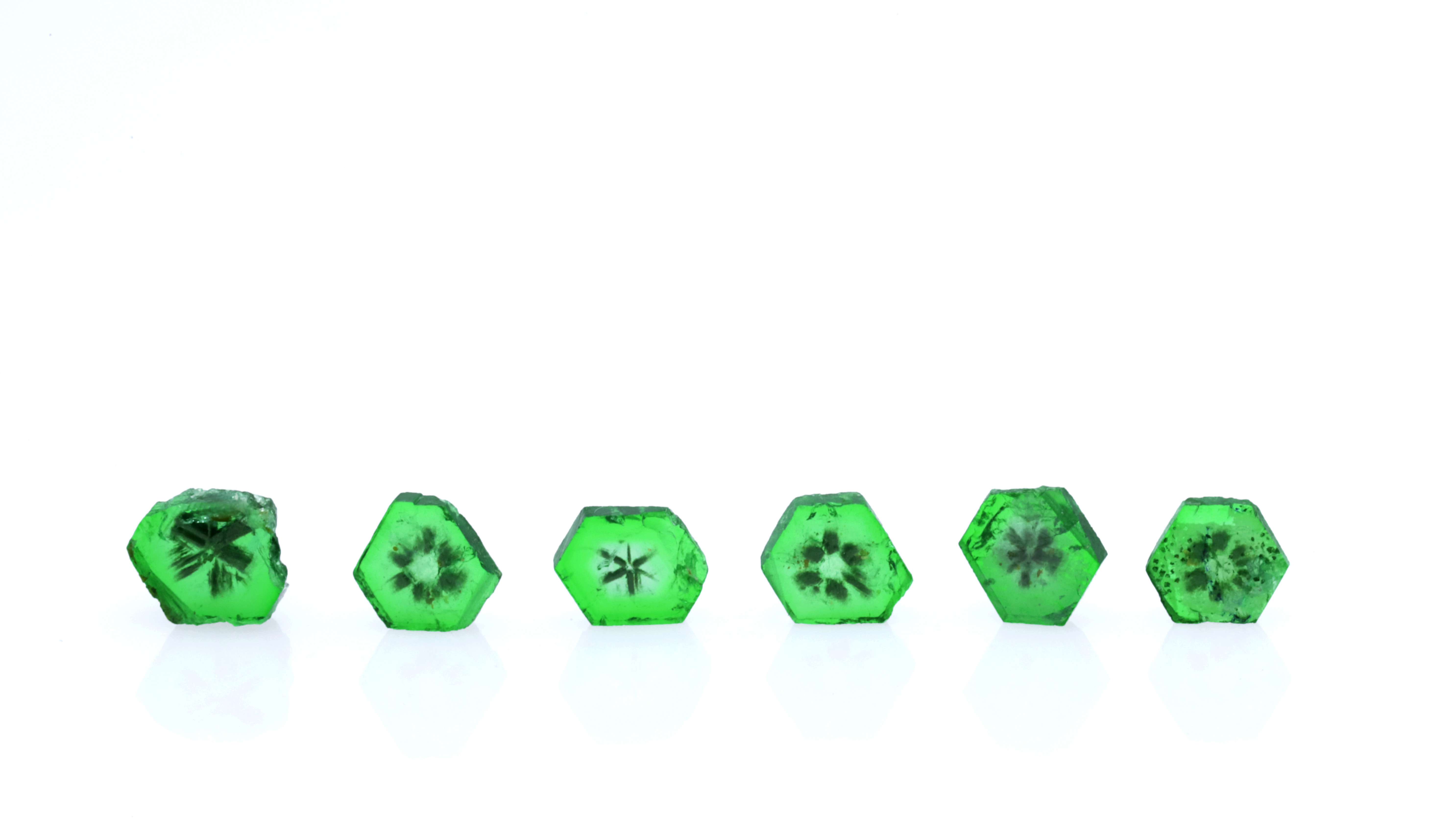
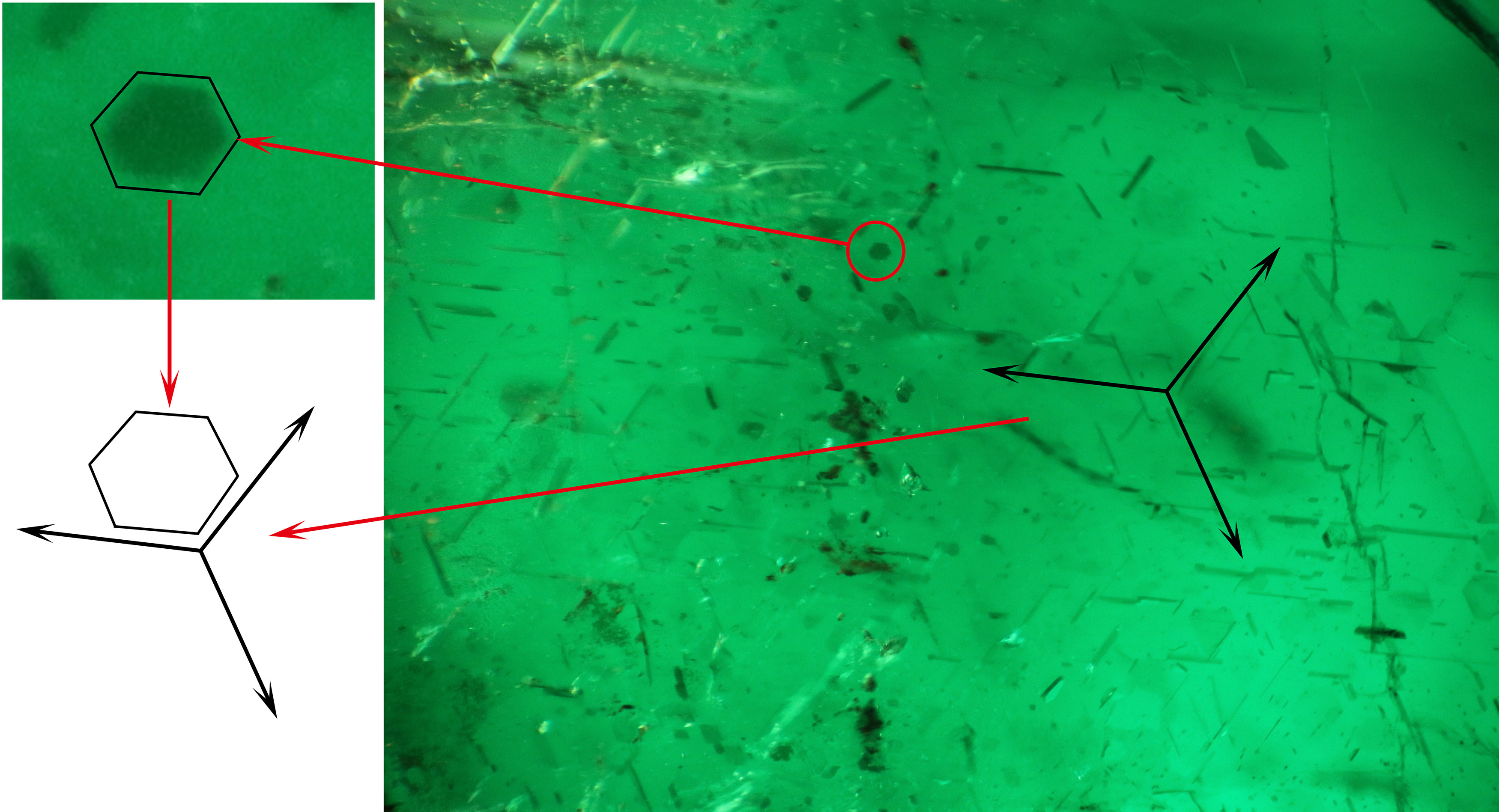
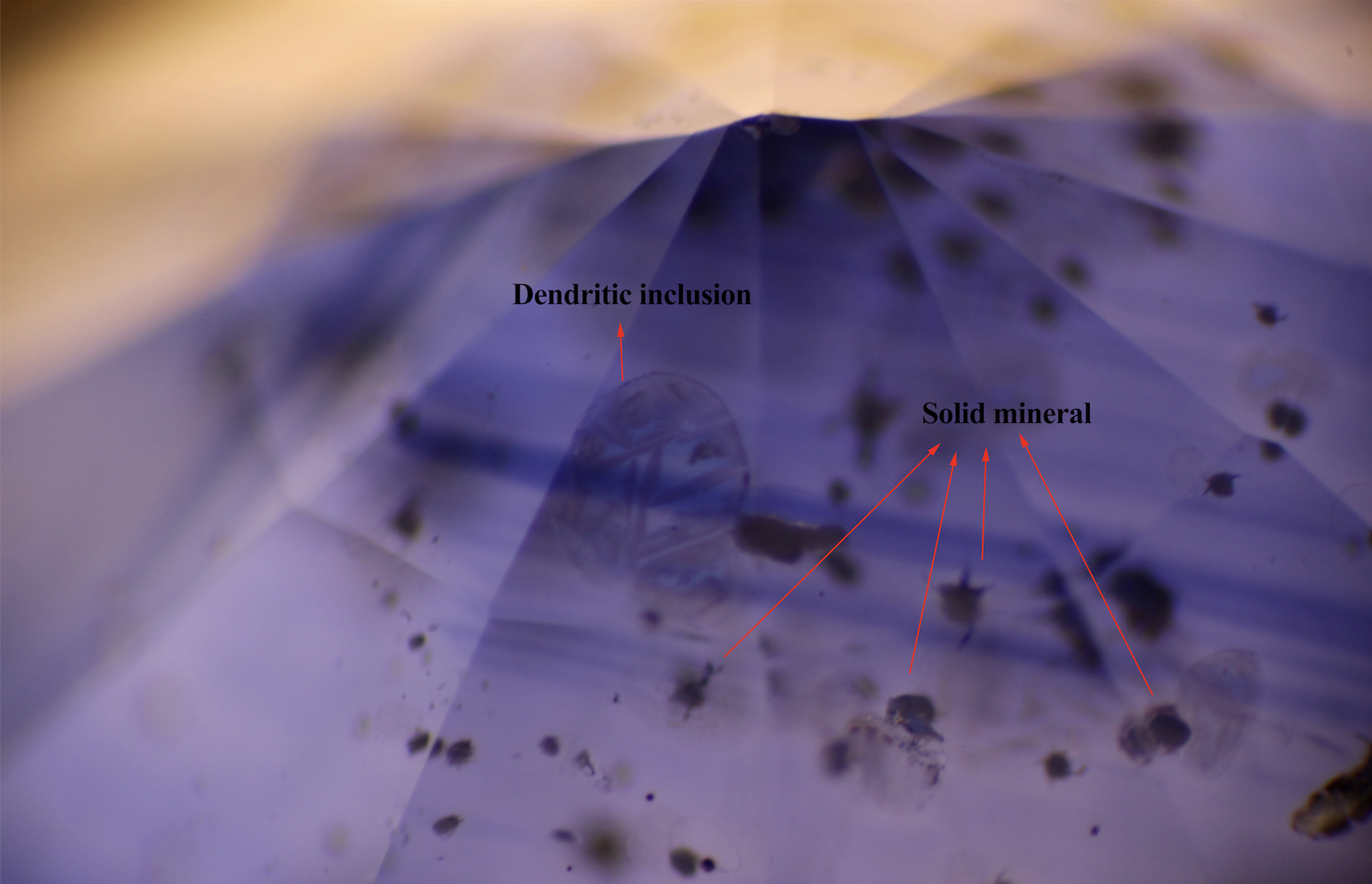
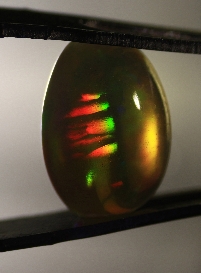
A Preliminary Discussion on the Water Absorbency of Hydrophane Opal from the Wollo Region, Ethiopia
In recent years, Ethiopian opals have rapidly flooded into the jewelry market, sparking widespread research interest. In this paper, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), Raman spectroscopy, and ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometry were used to conduct a spectroscopic analysis of Hydrophane opals from the Wollo region in Ethiopia, and they were compared with black opals, white opals, and water opals. In addition, the water absorbency was demonstrated through water immersion experiments. The results show that the infrared absorption peak near 1098 cm⁻¹ and the relatively strong absorption peak near 970 nm are effective bases for determining Hydrophane opals.